

The Public Distribution System (PDS) is a poverty alleviation programme in India and provides
“Food Security” for below poverty line population. It is one of the largest social safety net programs
in the world. Under PDS essential commodities like rice, wheat, sugar and kerosene are supplied to
targeted beneficiaries at affordable prices through the Fair Price Shops (FPS). The current format of PDS,
called the Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS) introduced in 1997, classifies beneficiaries in several
categories based upon income level and accordingly provides benefits to the beneficiaries.
Several problems have been identified in the management and administration of the
TPDS system in its current form, including
The Government of India is evaluating various alternatives to address these issues. The Feasibility Study for Introduction of Smart Cards for PDS Pilot, undertaken by CAL2CAL, was a Government of India, Ministry of Finance (Department of Economic Affairs) project and was sponsored by The World Bank, to evaluate the feasibility of introducing Smart Cards as a technology-based tool that will assist the TPDS administration to
CAL2CAL conducted several one-on-one meetings with key stake holders in the PDS chain and conducted on-site Focus Group
meetings with government officials and providers to establish the project baseline. The project was conducted in
selected areas of Thane and Anand.
The primary study involved extensive field interviews with the targeted beneficiaries of the PDS system,
as well as the FPS owners and other involved in the distribution chain. CALDSGTM, our ground breaking product
for dynamic generation of data collection Forms, was deployed on Palm® PDAs and extensively used to collect
data and responses in the field. Our professionals designed the questionnaire with the CALDSG DesignerTM and the
CALDSG Palm ComponentTM was used for electronic data collection in the field on Palm® devices.
The Operations team contacted the local youths of Gujarat and Maharashtra for the collection of
field data after briefing them on the PDS and providing necessary training to use Palm® devices
with CALDSGTM for data collection. The CALDSGTM Device and Data Management module was used to clean
and consolidate the data collected from the field and the same was tabled to our panel of domain experts for analysis.
Post Analysis results were translated as the Institutional Report and the Technical Report. The Institutional Report addressed
the policy and governance issues in implementing a Smart Card based system, while the Technical Report addressed the technical,
infrastructure, cost and training issues. A combined report with projected cost of implementing a Smart Card based system,
was tabled with the respective authorities to aid their process of decision making.
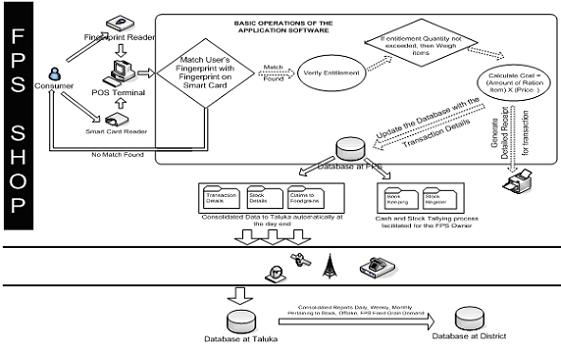
(a) The beneficiaries present their cards and are authenticated at the POS terminal and thereafter necessary sales are made.
(b) All sales, sales summary and stock balance reports will be available at the POS Terminal and the summary of these are
available in the SAM /Service smart card of the FPS owner, and the data is uploaded to the Taluka Server at the end of
the day (in an online system) or uploaded using the SAM/Service card (in an offline system).
(c) The allotment of rations to FPS is based on the stock details and consumption patterns
received online/offline from the FPS. This automatically stops manipulation of stock demand by FPS owners.
(d) Information flow is either online or smart card based, depending on the type of solution fielded.